A meme being shared on social media claims tumours exist in the body to save lives by gathering all the toxins together in one place.
Cancer specialists have told AAP FactCheck the claim is not true, also rejecting a second claim in the meme – that needle biopsies of tumours spread cancer around the body. An example of the meme is this Instagram post. It has also been shared on Twitter.
The meme states: “People need to understand that a tumour is there to save your life, When your body is full with poison, toxaemic and acidosis and you are basically going to die of that poison — your body builds a bag and collects all the poison from your body into this bag, which they call a tumour. So the body did all the work.”
Professor Michael Barton, a cancer specialist from UNSW’s faculty of medicine, told AAP FactCheck it was the most ridiculous collection of misinformation he had seen since “Donald Trump left office”.
“Tumours do not ‘save your life’,” Prof Barton said in an email. “They grow and can kill unless treated.”
Similarly, Professor Ian Olver of the University of Adelaide, a medical oncologist, cancer researcher and bioethicist, said tumours do not detoxify the body.
“Cancers are normal body cells that due to genetic changes no longer respond to signals to stop growing,” Prof Olver told AAP FactCheck in an email.
“They compete with normal cells for nutrients which is one of the ways they harm the body. They do not detoxify the body or protect the body from toxins. In the body, the liver and kidneys share that task.”
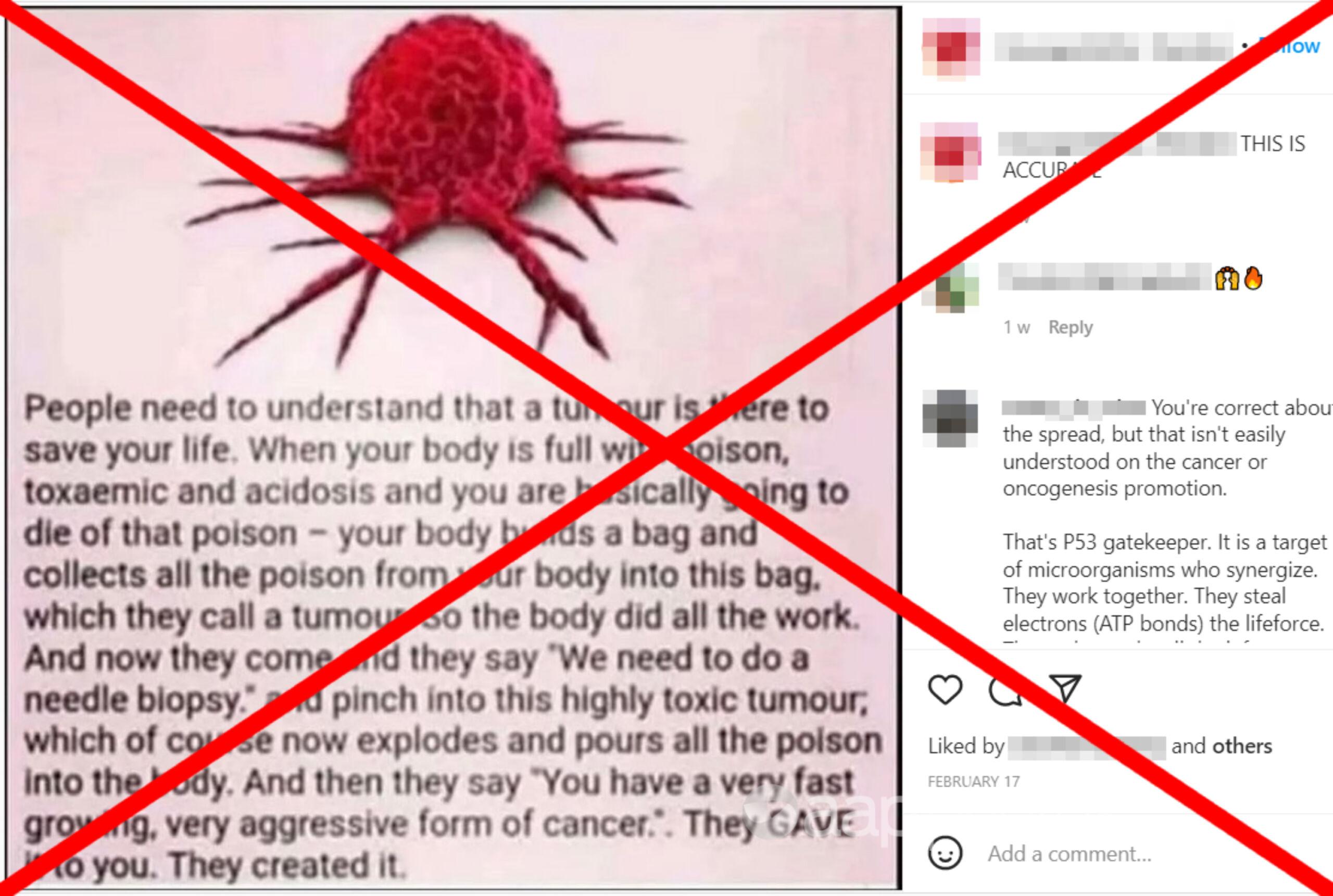
The meme also claims needle biopsies of tumours are dangerous because they cause the “toxic tumour” to explode, which results in the poison being poured into the body. It claims this results in a “very aggressive form of cancer”.
Prof Barton also rejected this claim, saying “needle biopsies are very safe”.
“They have been used for decades particularly for the diagnosis of breast, prostate and lung cancers,” he said.
The American Society of Clinical Oncology says a biopsy is often the best way to definitively say whether a person has cancer. It also describes an occurrence called “needle seeding“, a rare instance of biopsies spreading cancer.
The society says the idea gained traction following the publication of a book in 2012 by urologist Ronald Wheeler, whose medical licence was revoked in 2017. Dr Wheeler was convinced needle biopsies of prostate cancer spread cancer cells outside the prostate.
He was arrested in 2017 for defrauding patients and practising medicine without a licence, and found guilty in 2018.
Several studies have been published on tumour seeding in different types of cancer, such as liver cancer and pancreatic cancer (here and here), concluding that the incidence of needle tract tumour seeding following biopsies was either very low or that biopsies were not associated with an increased risk of seeding.
A 2019 study published in the journal Urology showed researchers concluded from a study of 42 patients with bladder cancer that needle biopsy did not cause tumour seeding.
Prof Olver said tumour seeding from a biopsy was extremely rare.
“Tumours spread by shedding cells into the circulation either early in their growth or late,” Prof Olver said.
“This can occur before they become visible. They certainly don’t need any mechanical disturbance like a biopsy for this to happen.
“It is very rare for a biopsy to be associated with spreading a tumour. However, there are rare cases where fine needle biopsies have been associated with seeding of tumour cells along the needle track.”
Prof Olver said the benefit of obtaining a definite cancer diagnosis on which to base treatment far outweighed the risk of these rare cases.
The Verdict
A social media meme claiming tumours detoxify the body is false, with one cancer specialist calling it ridiculous. Tumours are cells which do not stop growing and compete with healthy cells. The claim biopsies spread a tumour’s “poison” is also false. The incidence of “tumour seeding” by needle biopsy is rare. Cancer specialists and multiple scientific studies say it is a safe diagnostic tool.
False – The claim is inaccurate.
* AAP FactCheck is an accredited member of the International Fact-Checking Network. To keep up with our latest fact checks, follow us on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
All information, text and images included on the AAP Websites is for personal use only and may not be re-written, copied, re-sold or re-distributed, framed, linked, shared onto social media or otherwise used whether for compensation of any kind or not, unless you have the prior written permission of AAP. For more information, please refer to our standard terms and conditions.