AAP FACTCHECK – Sunglasses increase the risk of sunburn because they disrupt the body’s natural response to sunlight, according to alternative health advice being shared online.
This is false. Experts told AAP FactCheck that wearing sunglasses does not lead to an increased risk of sunburn.
The claim has appeared in multiple social media posts as the southern hemisphere nears the summer period.
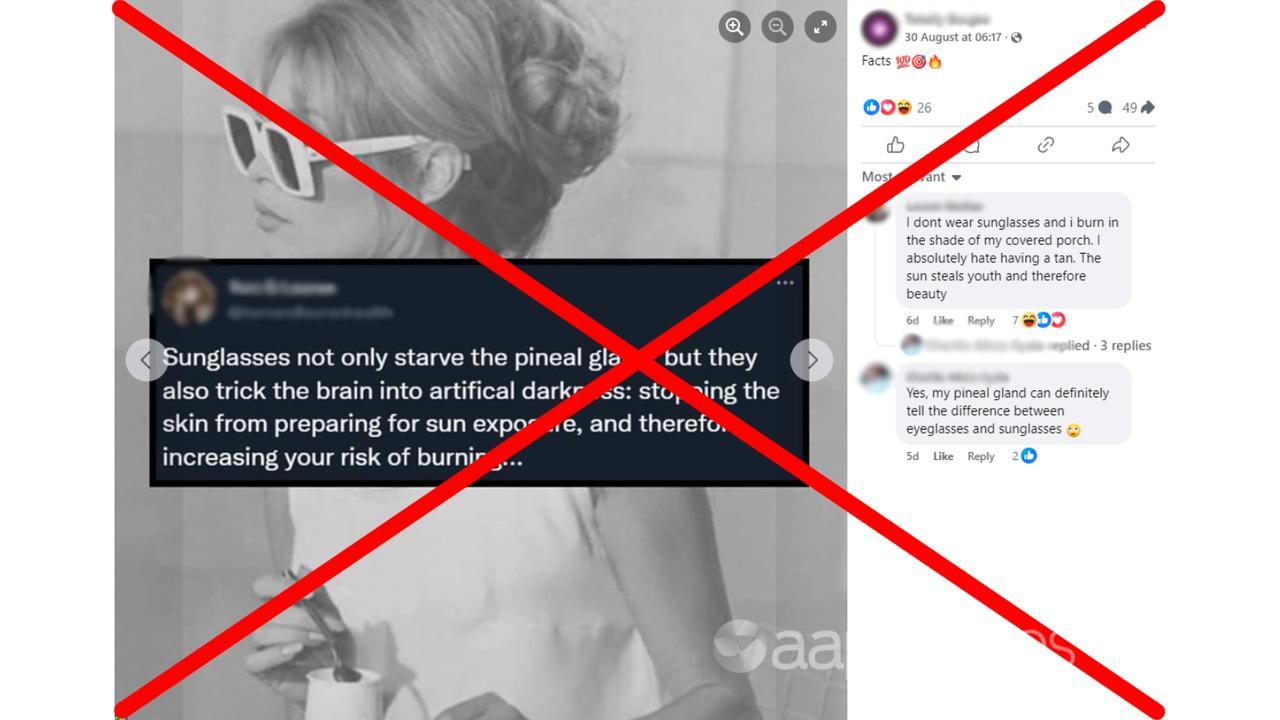
“Sunglasses not only starve the pineal gland, but they also trick the brain into artificial darkness: stopping the skin from preparing for sun exposure, and therefore increasing your risk of burning…” a screenshot of an X post shared in one Facebook post claims.
“Wearing sunglasses in the sun can lead to an increased risk of sunburn due to a potential disruption in the body’s natural response to sunlight,” reads the caption of another post.
The sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays stimulate melanocyte cells, found in deeper layers of the skin, to produce a pigment called melanin.
Melanin offers protection by absorbing UV light and redistributing it towards upper layers of skin, which is the process that causes a tan to develop.
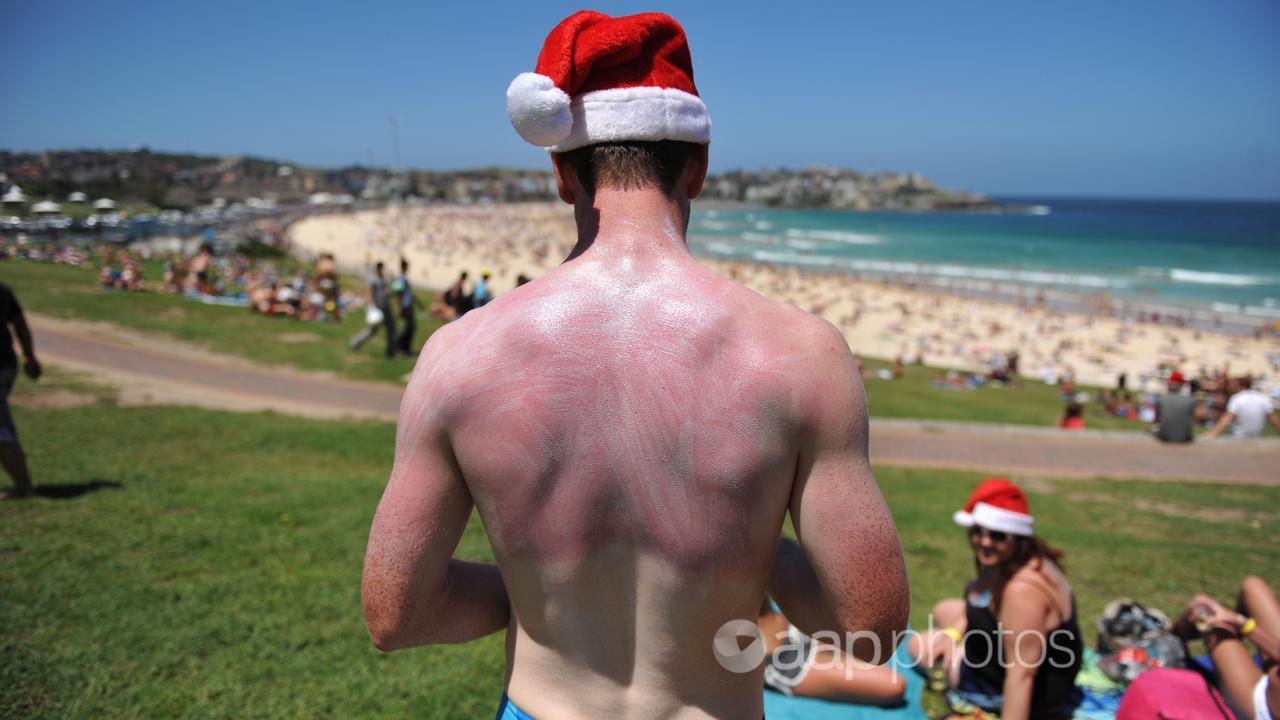
Sunburn occurs when UV rays exceed the level of protection melanin can provide.
David Whiteman, a medical epidemiologist at the QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute, told AAP FactCheck sunglasses reduce the transmission of UV light to the eye and its surrounding skin.
But he said “they have no effect on the production of melanin pigment at other sites of the body”.
He added: “These posts are almost medieval in their lack of basic understanding of photobiology.”
University of Adelaide’s Ian Olver said UV exposure on the skin alone will produce melanin anyway, regardless of whether you are wearing sunglasses.
He said there isn’t sufficient evidence to support the idea that covering the eyes will trick the body into thinking it is less exposed.
“Moreover, leaving the eyes unprotected increases their risk of UV damage out in the sun, so [they] should form part of sun protection when the sun’s intensity (which is measured and reported as ‘UV index’) is high.”

Anne Cust, chair of the Cancer Council’s national Skin Cancer Committee, said wearing sunglasses does not increase the risk of getting sunburnt.
The sun’s UV radiation is the main source of skin cancer, and overexposure over long periods can lead to permanent damage of the eyes, including skin cancer around the eyes and ocular melanoma.
“Wearing sunglasses reduces the reflected UV radiation and glare from the sun,” Professor Cust said.
Professor Olver noted that sunglasses are recommended as part of overall sun protection, which includes using sunscreen, wearing a hat and sun-protective clothing, and seeking shade when UV levels are high.
The claim that sunglasses increase the risk of sunburn has also been debunked by Full Fact.
The Verdict
False – The claim is inaccurate.
AAP FactCheck is an accredited member of the International Fact-Checking Network. To keep up with our latest fact checks, follow us on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
All information, text and images included on the AAP Websites is for personal use only and may not be re-written, copied, re-sold or re-distributed, framed, linked, shared onto social media or otherwise used whether for compensation of any kind or not, unless you have the prior written permission of AAP. For more information, please refer to our standard terms and conditions.


















